Hepatitis B new drug clinical phase 2 obtained positive results
Hepatitis B new drug clinical phase 2 obtained positive results
November 29, 2017 Source: WuXi PharmaTech
Window._bd_share_config={ "common":{ "bdSnsKey":{ },"bdText":"","bdMini":"2","bdMiniList":false,"bdPic":"","bdStyle":" 0","bdSize":"16"},"share":{ }};with(document)0[(getElementsByTagName('head')[0]||body).appendChild(createElement('script')) .src='http://bdimg.share.baidu.com/static/api/js/share.js?v=89860593.js?cdnversion='+~(-new Date()/36e5)];Recently, Spring Bank Pharmaceuticals, which specializes in the development of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection therapy, announced the top-line results of Part A of the second cohort (50 mg, monotherapy) of the ongoing "ACHIEVE" clinical phase 2 trial. The company is developing a selective immunomodulator inarigivir for oral administration as an important component of combination therapy for patients with chronic HBV infection, with the goal of significantly improving functional cure rates in a simple, safe and selective manner. The primary endpoint of Part A of the ACHIEVE clinical trial was to assess drug safety and antiviral activity as indicators of changes in HBV DNA relative to baseline at 12 weeks of treatment, as well as multiple exploratory secondary endpoints. All patients in this cohort have been converted to 300 mg daily for 12 weeks of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate therapy.

About 257 million people worldwide are infected with hepatitis B virus ("HBV"), including about 17 million people in the United States and Europe. The virus causes liver disease to progress, with approximately 887,000 deaths each year. At present, there are relatively few new therapies for HBV research. Existing standards of care require the use of chronic treatment with antiviral therapy to inhibit the HBV virus. Although there are effective vaccines to prevent hepatitis B infection, there is still a need to improve HBsAg clearance and treatments that may lead to cure.
The second cohort of the trial included 18 evaluable patients, 14 of whom were in the inarigivir 50 mg treatment group (10 HBeAg-positive, 4 HBeAg-negative) and 4 in the placebo group. In the inarigivir treatment group, the patient was well tolerated by inarigivir and no serious adverse reactions occurred. Compared with the placebo group, the inarigivir treatment group showed a statistically significant reduction in HBV DNA at week 12 with an average reduction of 0.74 log10 (p = 0.0008). Compared with placebo, HBeAg-negative patients had an average reduction of HBV DNA of 1.05 log10 (p = 0.01) and HBeAg-positive patients had an average reduction of 0.61 log10 (p = 0.006).
The secondary endpoint of this cohort also showed positive results: for the secondary endpoint of HBV RNA reduction, the treatment group (mean reduction of 0.95 log10, p = 0.03) was also significantly better than placebo (mean increase of 0.48 log10), and HBeAg-negative patients The effect was more pronounced; in addition, when comparing HBV DNA and HBV RNA in the first cohort (25 mg) and the second cohort (50 mg), the second cohort showed a dose-dependent decrease; for HBV surface antigen (HBsAg) reduction At this secondary endpoint, HBsAg in a HBeAg-positive patient in the treatment group continued to decrease by more than 0.5 log10. HBV RNA was not detected in all 4 HBeAg-negative patients at week 12, but there was no significant decrease in HBsAg, suggesting that patients with HBsAg may be mainly derived from intensive HBV DNA.
When the patients in the first and second cohorts of the ACHIEVE trial were combined, the patients were grouped by baseline viral (6 log10) or HBsAg (4 log10), and the primary endpoint of "HBV DNA reduction" was Analysis showed a very significant positive correlation between the initial baseline viral load and HBV DNA reduction and was independent of HBeAg status.
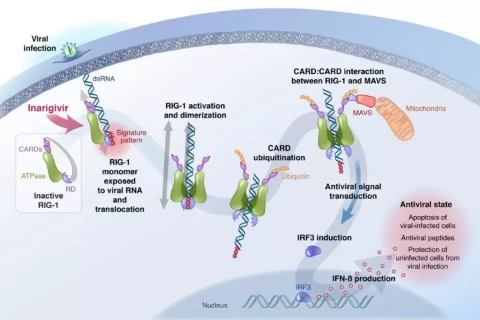
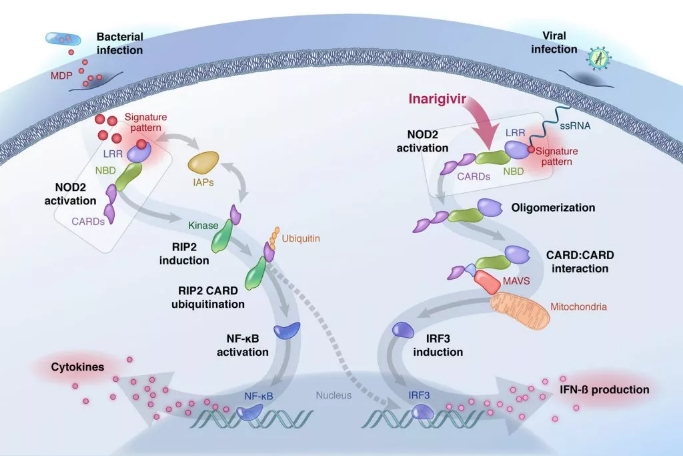
â–² Inarigivir initiates a dual antiviral mechanism: inhibition of viral replication, Inarigivir in combination with RIG-I prevents viral polymerases from participating in viral RNA replication; promotes viral clearance, and activated RIG-I induces endogenous IFN production. (Source: Spring Bank Pharmaceuticals official website)
Professor Stephen Locarnini, head of research and molecular development at the Victorian Infectious Diseases Reference Laboratory, said that we have seen low-dose inarigivir for HBV DNA and HBV RNA. A dose-dependent antiviral effect, which is consistent with possible inhibition of pgRNA encapsidation, but has not yet seen a complete immune response by inarigivir."
Spring Bank has initiated the third cohort (100mg) clinical trial of Part A of the ACHIEVE study and is expected to receive top-line results in the second quarter of 2018.
It is understood that Spring Bank has reached a clinical cooperation agreement with Gilead Sciences. In accordance with the collaboration, Gilead Sciences is responsible for conducting a Phase 2 trial to evaluate patients with chronic HBV who are co-administered with inarigivir and tenofovir levamide (trade name Veclidy). Similar to the ACHIEVE study Part A, the Phase 2 clinical trial protocol will include a 12-week study of inarigivir (50 mg) and Vemlidy combination therapy, after which all patients will be switched to a 12-week Vemlidy monotherapy. Spring Bank expects Gilead Sciences to conduct this clinical trial in the first quarter of 2018.
“We are pleased to announce that in the ACHIEVE trial, the daily cohort of 50 mg inarigivir for the second cohort, we achieved the primary end point of safety and efficacy in the 12-week test,†Dr. Nezam Afdhal, Chief Medical Officer, Spring Bank "The response to HBV DNA and HBV RNA in patients with antiviral doses of inarigivir that are not associated with a complete immune response is encouraging," the results support further research and development, and we are developing to include inarigivir The combination of therapy as a potential backbone treatment program, the ultimate goal is to improve the functional cure rate of hepatitis B patients."
Reference materials:
[1] Spring Bank Pharmaceuticals official website
[2] Spring Bank Pharmaceuticals Announces Positive Top-Line Results from the Second Cohort of Part A of the Phase 2 ACHIEVE Trial
Nitrogen Cylinder,Green Nitrogen Gas Cylinder,Green Nitrogen Cylinder Bottles,Nitrogen Cylinder Bottles
JIANGSU NEW FIRE FIGHTING TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.newayfire.com