Nature Subsidiary: Revealing the Role of lncRNA in EMT
José A Pintor-Toro, a professor at the University of Sélivia in Spain , has long been engaged in biochemistry and cell biology research. Recently, his laboratory used the Arraystar LncRNA chip to discover the TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process. Lnc-Spry1, a lncRNA molecule that plays a direct regulatory role in the early stage, directly induces down-regulation of lnc-Spry1, which triggers the EMT process to affect cell invasion and migration. lnc-Spry1 also interacts with U2AF65, affecting variable splicing, thereby regulating gene expression at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. The research results were published in the cell death journal Cell Death & Differentiation (IF: 8.218) (chip experiments provided by Arraystar)
Research Background
The epithelial-mesenchymal cell transformation (EMT) process is a fundamental cellular phenotypic transition process. During the period, epithelial cells lose intercellular tight junctions and adhesion to the basement membrane, transform into interstitial cells, and acquire invasion and migration activities. At the transcriptional level, TGF-β directly activates the EMT process, leading to changes in downstream pathways and a range of gene expression. In addition, the alternative splicing of pre-mRNA and the regulation of lncRNA also increase the complexity of the regulatory level at the post-transcriptional level. As an important regulatory RNA molecule, LncRNA can affect the EMT process at multiple levels. The existing articles only study the lncRNA downstream of TGF-β signal and affect cell stability. The purpose of this paper is to find the lncRNA molecule that plays a direct role in the early regulation of EMT.
The epithelial-mesenchymal cell transformation (EMT) process is a fundamental cellular phenotypic transition process. During the period, epithelial cells lose intercellular tight junctions and adhesion to the basement membrane, transform into interstitial cells, and acquire invasion and migration activities. At the transcriptional level, TGF-β directly activates the EMT process, leading to changes in downstream pathways and a range of gene expression. In addition, the alternative splicing of pre-mRNA and the regulation of lncRNA also increase the complexity of the regulatory level at the post-transcriptional level. As an important regulatory RNA molecule, LncRNA can affect the EMT process at multiple levels. The existing articles only study the lncRNA downstream of TGF-β signal and affect cell stability. The purpose of this paper is to find the lncRNA molecule that plays a direct role in the early regulation of EMT.
Research ideas
In order to explore the lncRNA molecules that directly affect early regulation during EMT, this study used US Arraystar mouse LncRNA chip to screen the differentially expressed lncRNA and mRNA of TGF-β induced NMuMG cell line 2h. Among them, 435 lncRNA and 1090 mRNAs showed significant differences. Then, Spry1 with down-regulation was selected and studied near lncRNA-lnc-Spry1. qPCR confirmed that the expression trend was consistent with the chip.
Functional studies of this lncRNA revealed that the molecule began to down-regulate 15 min after TGF-β induction, indicating an early regulatory molecule. After knocking out Smad4, lnc-Spry1 changes significantly, so the lncRNA molecule is TGF-β-Smad. A pathway-dependent target gene. The molecule was subjected to shRNA knockout assay and found that the markers of villin and Snail1 were elevated, and the marker E-cadherin of epithelial cells was decreased, resulting in migration and invasion phenotypic changes, indicating that lnc-Spry1 can remodel the cytoskeleton and affect cells. Migration and invasion.
By studying the expression of lnc-Spry1 and the adjacent gene Spry1, it was found that they had expression correlation. High-throughput detection and GO analysis were performed after knocking out lnc-Spry1, and it was found that chemokines and cytokine-related genes changed significantly. Furthermore, the mechanism of lnc-Spry1 was studied. Through RIP and RNA pull down technology, it was found that lnc-Spry1 can bind to the variable splicing-related protein U2AF65, thus affecting the variable splicing process of EMT transformation-related gene FGFR pre-mRNA.
In order to explore the lncRNA molecules that directly affect early regulation during EMT, this study used US Arraystar mouse LncRNA chip to screen the differentially expressed lncRNA and mRNA of TGF-β induced NMuMG cell line 2h. Among them, 435 lncRNA and 1090 mRNAs showed significant differences. Then, Spry1 with down-regulation was selected and studied near lncRNA-lnc-Spry1. qPCR confirmed that the expression trend was consistent with the chip.
Functional studies of this lncRNA revealed that the molecule began to down-regulate 15 min after TGF-β induction, indicating an early regulatory molecule. After knocking out Smad4, lnc-Spry1 changes significantly, so the lncRNA molecule is TGF-β-Smad. A pathway-dependent target gene. The molecule was subjected to shRNA knockout assay and found that the markers of villin and Snail1 were elevated, and the marker E-cadherin of epithelial cells was decreased, resulting in migration and invasion phenotypic changes, indicating that lnc-Spry1 can remodel the cytoskeleton and affect cells. Migration and invasion.
By studying the expression of lnc-Spry1 and the adjacent gene Spry1, it was found that they had expression correlation. High-throughput detection and GO analysis were performed after knocking out lnc-Spry1, and it was found that chemokines and cytokine-related genes changed significantly. Furthermore, the mechanism of lnc-Spry1 was studied. Through RIP and RNA pull down technology, it was found that lnc-Spry1 can bind to the variable splicing-related protein U2AF65, thus affecting the variable splicing process of EMT transformation-related gene FGFR pre-mRNA.
Technical route
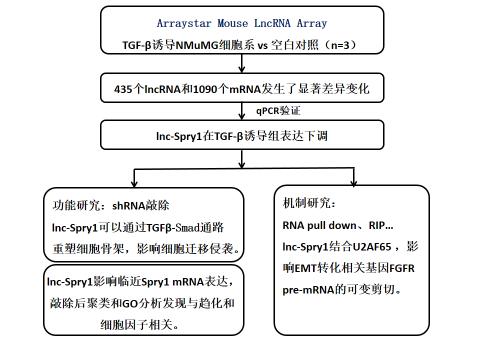
Result display
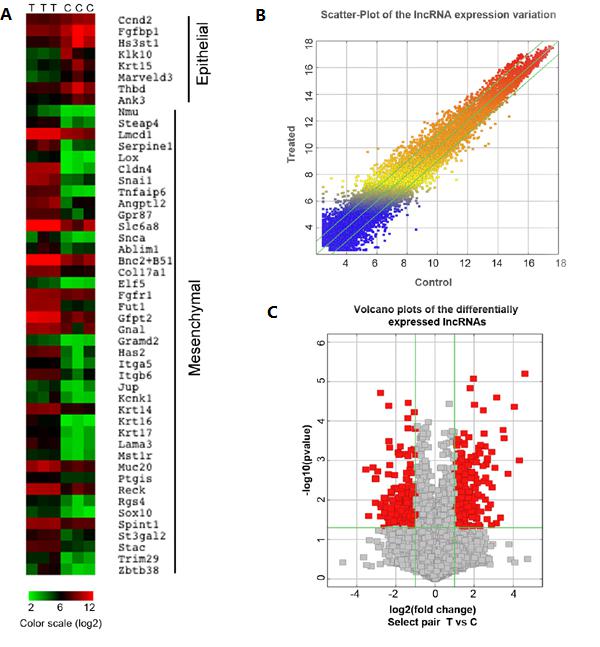
Figure 1. A: EMT-related genes with significant changes in chip detection after TGF-β treatment; B: scatter plots of lncRNA distribution with significant changes in chip detection after TGF-β treatment; C: chip detection after TGF-β treatment 2, P<0.05 lncRNA distribution volcano map;
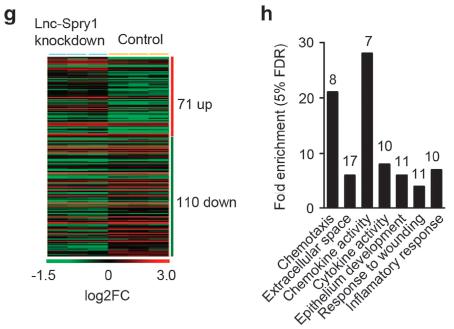
Figure 2. g. Lnc-spry1 knockout analysis of gene expression clustering map; h. Lnc-spry1 knockout after GO analysis, found that enriched GO entries are related to chemokines and cytokines.
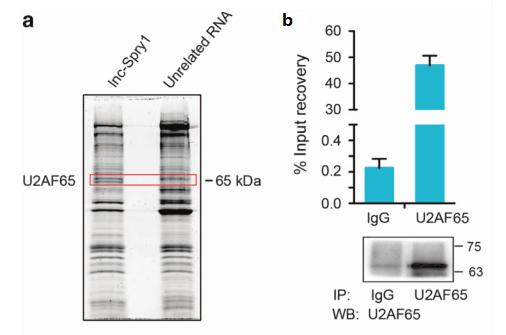
Figure 3. a. RNA pull down combined with mass spectrometry Lnc-spry1 can bind U2AF65; b. RIP experiment U2AF65 can bind Lnc-spry1.
Significance
This study revealed a relationship between lnc-Spry1 and TGF-β-induced early regulation of EMT. TGF-β induced NMuMG cells to directly down-regulate lnc-Spry1, and remodel the cytoskeleton through TGFβ-Smad pathway, affecting cell migration and invasion. lnc-Spry1 binds to U2AF65 and affects the variable cleavage of the EMT transformation-related gene FGFR pre-mRNA. Thereby regulating gene expression at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels.
This study revealed a relationship between lnc-Spry1 and TGF-β-induced early regulation of EMT. TGF-β induced NMuMG cells to directly down-regulate lnc-Spry1, and remodel the cytoskeleton through TGFβ-Smad pathway, affecting cell migration and invasion. lnc-Spry1 binds to U2AF65 and affects the variable cleavage of the EMT transformation-related gene FGFR pre-mRNA. Thereby regulating gene expression at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels.
about the author
José A Pintor-Toro, Ph.D. Professor of Signal Transduction Division, Center for Biomolecular and Regenerative Medicine, University of Selivia, Spain. He has long been engaged in plant, biochemistry and cell biology research, and his research results have been published in international authoritative academic journals such as Nature Genetics, PNAS, Nucleic Acids Research, Cell Death & Differentiation.
José A Pintor-Toro, Ph.D. Professor of Signal Transduction Division, Center for Biomolecular and Regenerative Medicine, University of Selivia, Spain. He has long been engaged in plant, biochemistry and cell biology research, and his research results have been published in international authoritative academic journals such as Nature Genetics, PNAS, Nucleic Acids Research, Cell Death & Differentiation.
Original source
Downregulation of Lnc-Spry1 mediates TGF-β-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition by transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulatory mechanisms. Cell Death and Differentiation. 2017.
Downregulation of Lnc-Spry1 mediates TGF-β-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition by transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulatory mechanisms. Cell Death and Differentiation. 2017.
Sea Shrimp Series,Pink Shrimp,Headless Pink Shrimp,Headless Ramboo Prawn
GOLD STAR FISHERY ZHOUSHAN CO.,LTD. , https://www.goldstar-aquatic.com